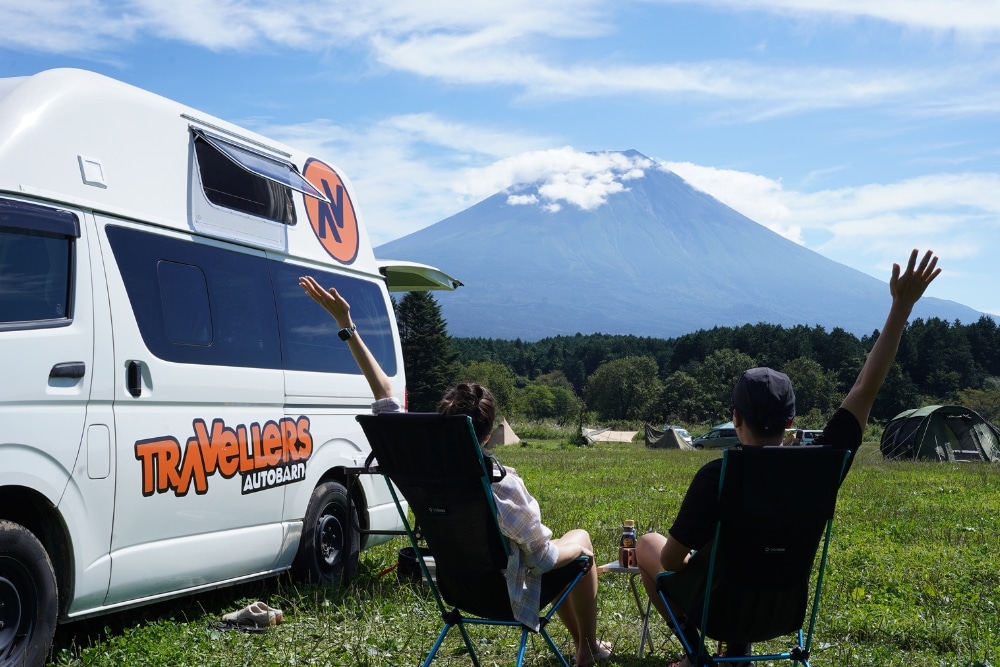
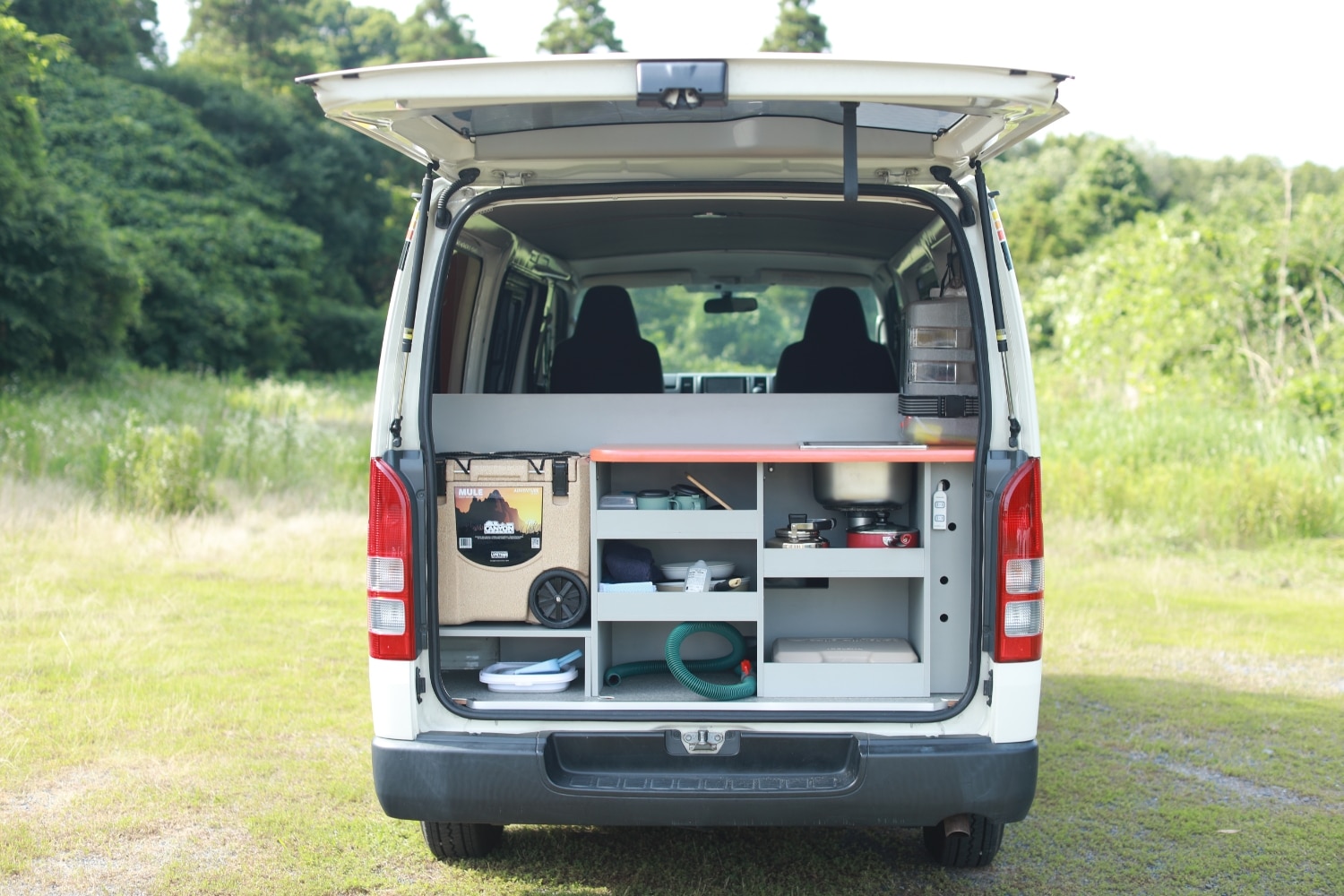
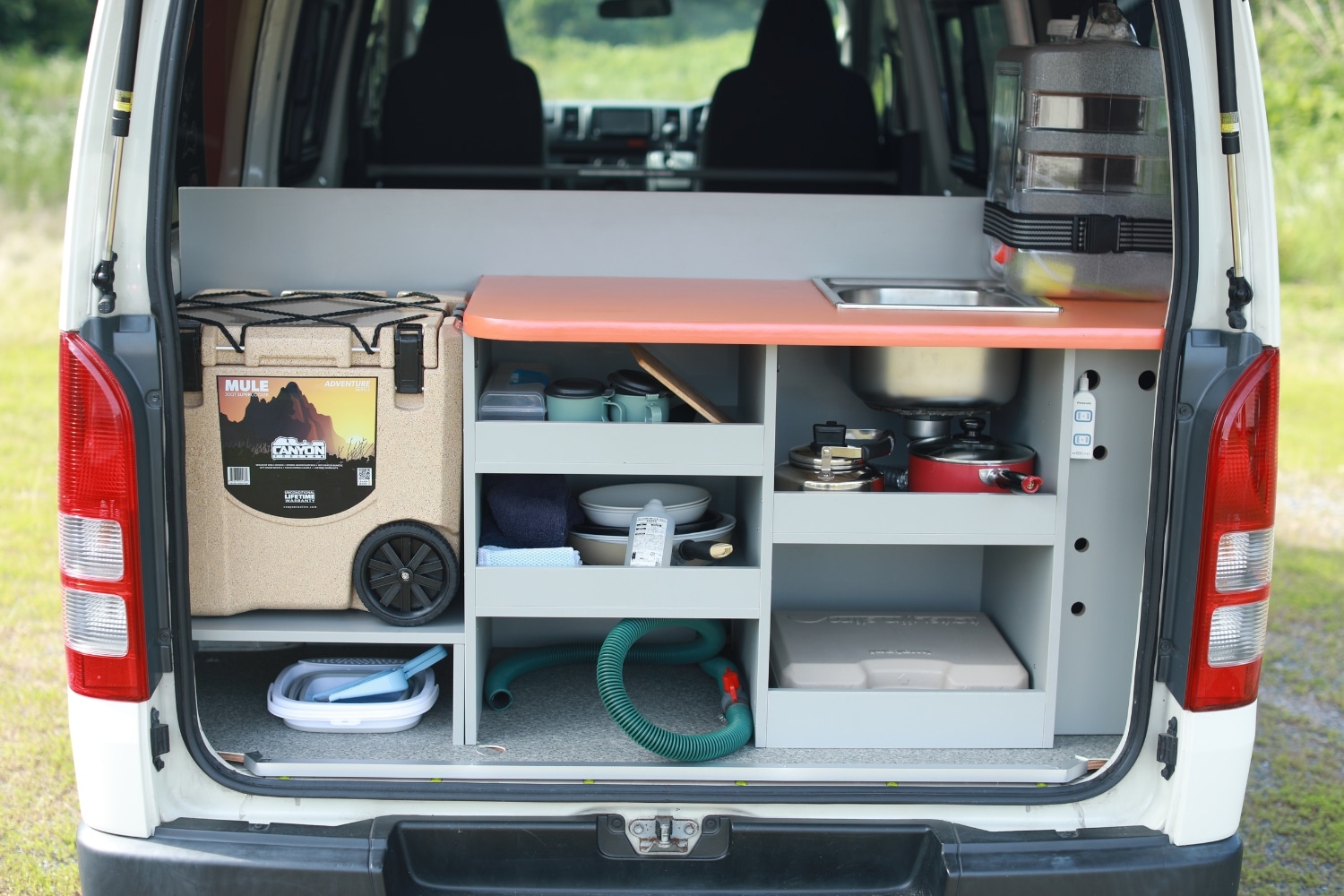
If you are planning a road trip to Japan, what do you expect from your trip? Natural scenery, historical culture, festivals, hot springs, hiking, camping, foods, crafts, etc. If you are coming to Japan, you may first learn about 8 areas of Japan and its unique characteristics, so that you can plan your itinerary and focus on the places you want to visit to create the best memories.
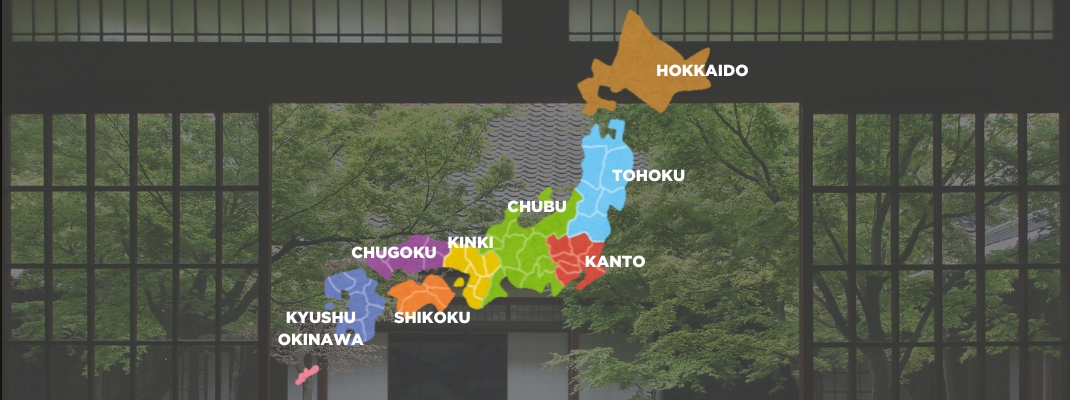
Discovering the 8 regions of Japan
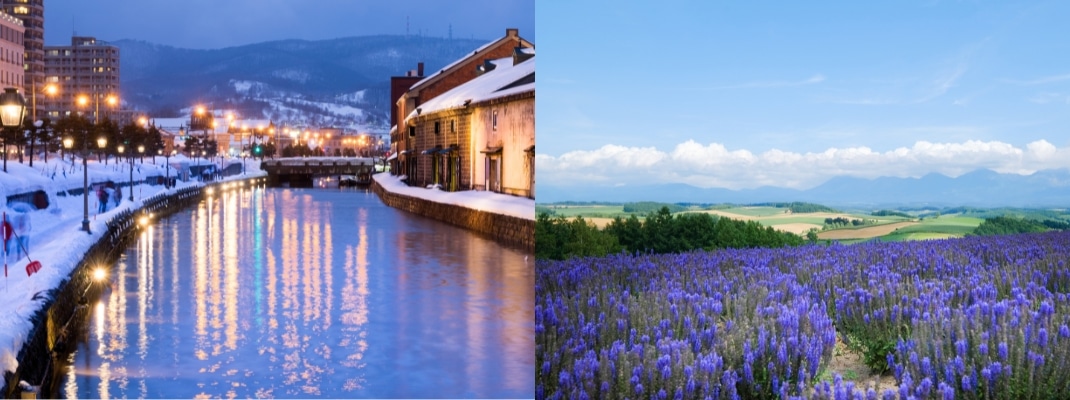
HOKKAIDO
Hokkaido is the most northerly island in the Japanese archipelago and winters are very cold and snowy. The average summer temperature is 22.3 degrees Celsius, making it a great place to spend the hottest months of the year. The population is approximately 5.3 million, with the largest city being Sapporo. Hokkaido is divided into 4areas. Dohoku(North), Doou(Central), Dotou(East), Donan(South).
The fishing industry is also very active. Some of the world’s most important fishing grounds lie around Hokkaido. Marine products such as scallops and kelp are farmed.
Hokkaido is one of Japan’s most popular tourist destinations, where you can enjoy nature on a grand scale, including the World Natural Heritage Site Shiretoko, the magnificent and varied mountains and the Kushiro Marshland, home to a diverse range of flora and fauna. The summers are cool and pleasant, and although the winters are cold, you can enjoy winter sports in Hokkaido’s superb snow conditions that can only be experienced in Hokkaido.
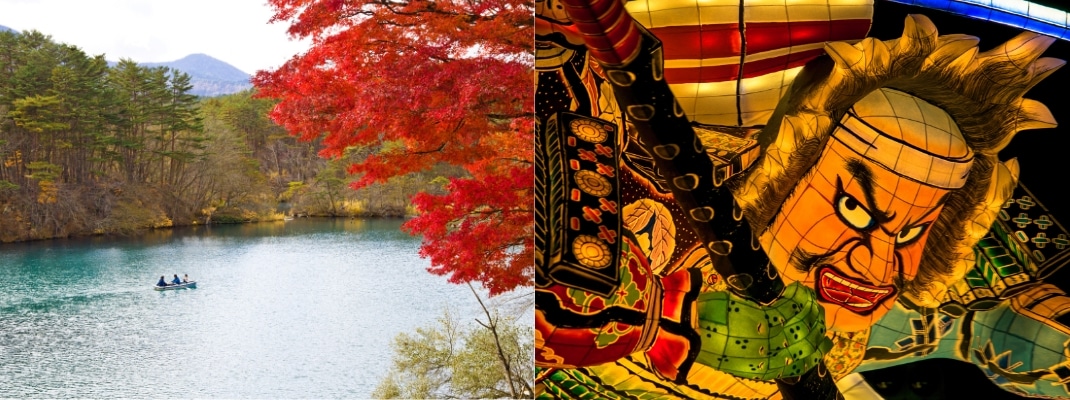
TOHOKU
The Tohoku region, with some of the most beautiful nature and numerous cultural heritage sites in Japan, is an area full of attractions that are still unknown to many tourists. The Tohoku region comprises six prefectures – AOMORI, IWATE, MIYAGI, YAMAGATA, AKITA and FUKUSHIMA – and is home to some 8.7 million people. Due to its high latitude, temperatures are lower than in the Kanto region and southwards, and beautiful snowy landscapes in many parts of the country in winter.
The Tohoku region offers a wide range of attractions, including two World Heritage Sites, the Shirakami Mountains in Aomori Prefecture and Hiraizumi in Iwate Prefecture, as well as spots where you can enjoy the beauty of nature, cultural assets that remind you of history and tradition, and hot spring towns full of emotion. It attracts many tourists in search of natural beach and oak forests and beautiful coastlines. Tourists flock to the three major summer festivals (Nebuta Festival in Aomori Prefecture, Kanto Festival in Akita Prefecture and Tanabata Festival in Sendai, Miyagi Prefecture).
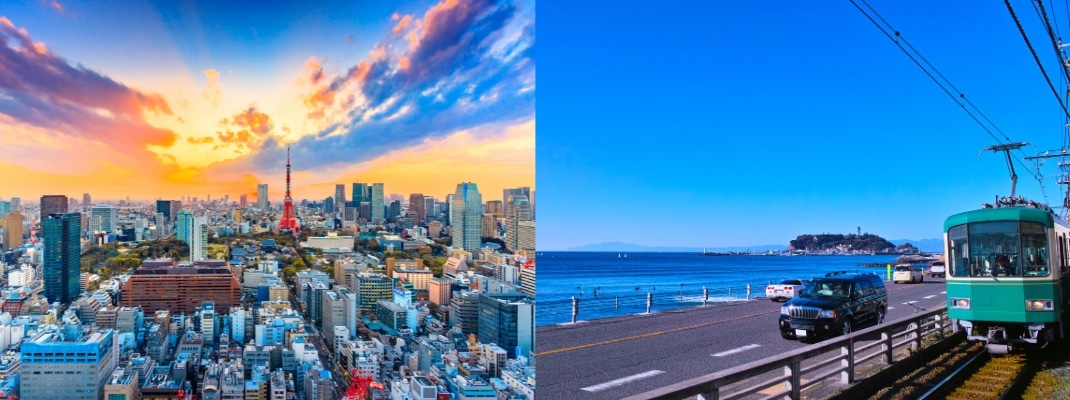
KANTO
The Kanto region, comprising Tokyo and the six prefectures of Ibaraki, Tochigi, Gunma, Saitama, Chiba and Kanagawa, is home to 43.3 million people, or about 34% of the total population of Japan. As the capital of Japan, Tokyo is home to many companies, government buildings, universities and other institutions.
The area is covered with plains, with mountainous regions to the north-west and the Pacific Ocean to the south-east. It has bays such as Tokyo Bay and Sagami Bay, and is characterised by the Boso and Miura Peninsulas. Summers are humid and winters dry.
Kanto has fashionable downtown areas such as Ginza and Shibuya, and there are many historical sites and tourist attractions, including Tokyo’s Senso-ji Temple, Yokohama with its international trading port, the ancient capital Kamakura and Nikko Toshogu Shrine, which is registered as a World Heritage Site.
Diverse cultural events and festivals are held throughout the year.
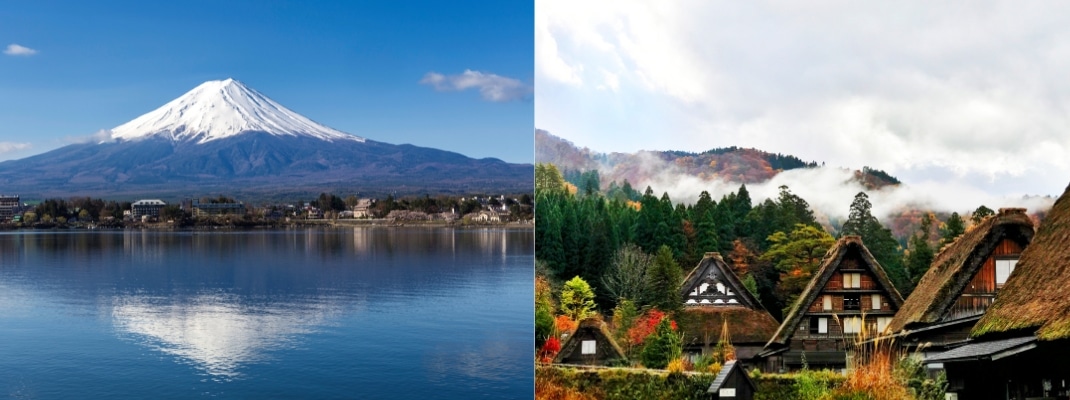
CHUBU
The Chubu region is wide in scope and is divided into three regions: the Hokuriku region on the Sea of Japan side, the Central Highlands and the Tokai region on the Pacific Ocean side. and The nine prefectures of the Chubu region are home to 21.35 million people. Shizuoka and Aichi, have a mild climate, while Yamanashi, Nagano and Gifu have high mountains in the middle of the region. The four prefectures facing the Sea of Japan – Fukui, Ishikawa, Toyama and Niigata – are known for their heavy snowfall.
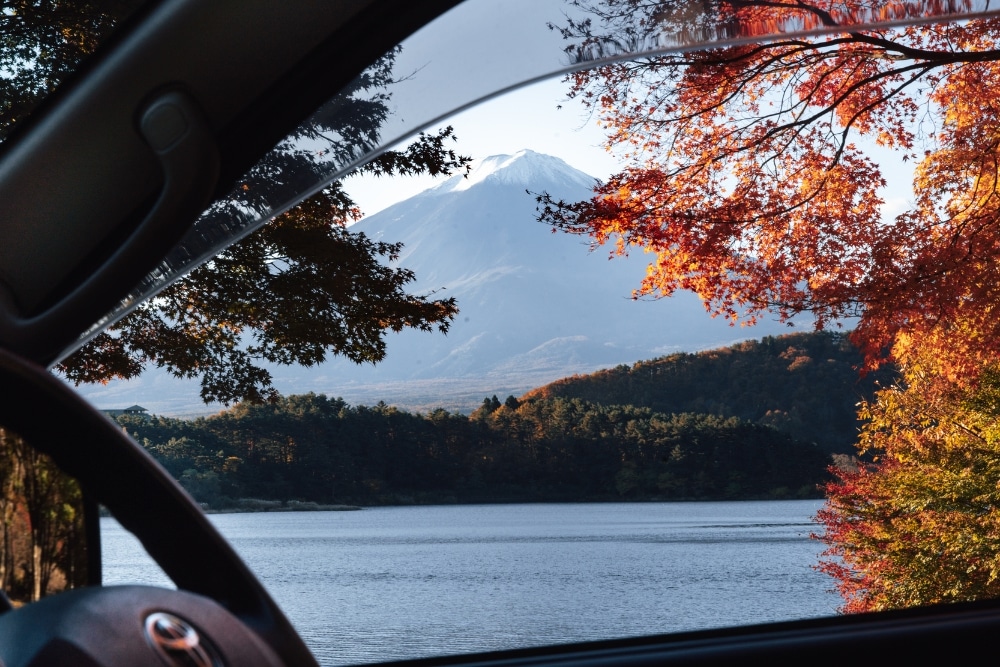
The central part of the Chubu region is lined with mountains in the 3000 m class. They are called the Japanese Alps. Straddling Shizuoka and Yamanashi prefectures is Japan’s highest volcano, Mt Fuji, at 3,776 metres.
Kanazawa city has many historical buildings and beautiful gardens, such as Kenrokuen Garden and Kanazawa Castle.
The Chubu region, located roughly in the middle of Honshu, has many areas such as Tsumago and Shirakawago, where traditional townscapes still remain,all of which retain beautiful landscapes.
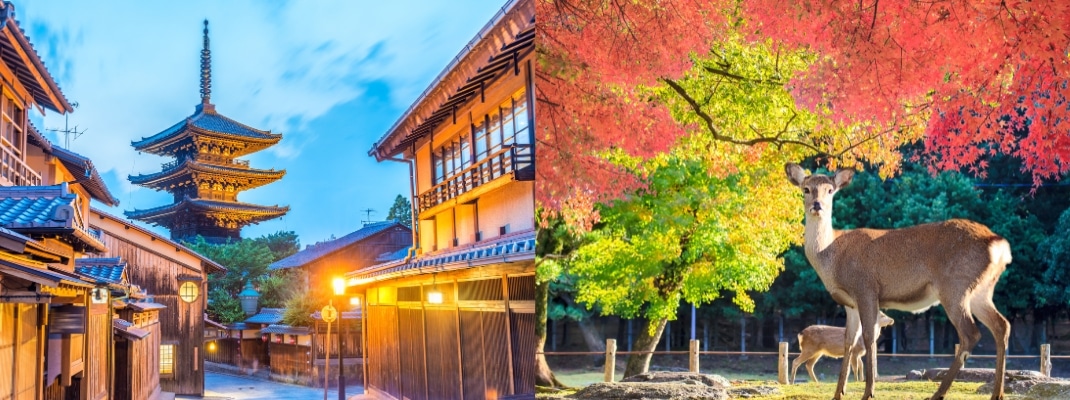
KINKI
The Kinki region comprises seven prefectures – Mie, Shiga, Nara, Wakayama, Kyoto, Osaka and Hyogo – and is home to approximately 22.4 million people, or 18% of Japan’s total population. The Kinki region was the capital of Japan for more than 1,000 years and is characterised by the large amount of traditional culture that remains in various parts of the country. About a quarter of the World Heritage Sites registered in Japan are located here, and the region is home to many national treasures and important cultural assets. You can also trace the origins of traditional Japanese culture, such as samurai culture, garden culture, Zen and the tea ceremony.
The Kinki region is home to many famous tourist attractions, including Osaka, Kyoto and Nara prefectures. Kyoto and Nara are renowned as the country’s capitals and places that played various historical roles from long ago until the Meiji Restoration of 1868. They are home to shrines, temples, Buddhist statues, paintings and other cultural assets of historical importance and attract many tourists from all over the world.
The Kii Peninsula, far from Kyoto and Osaka, is dotted with attractive tourist attractions such as Koyasan, the sacred site of Japanese Buddhism, the Kumano Kodo, a road of prayer dating back to ancient times, and hot springs. Along the coast to the west are the hot spring resort of Shirahama and areas where magnificent natural scenery and traditional culture coexist.
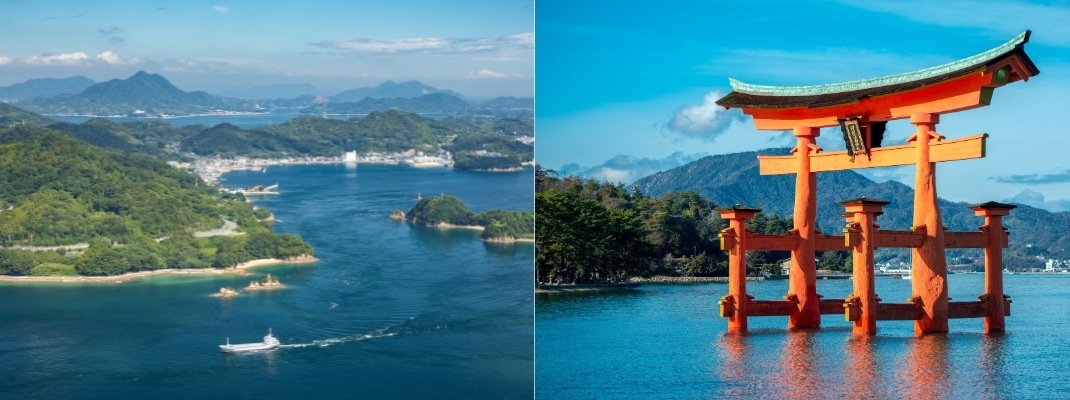
CHUGOKU
The Chugoku region, which occupies the western part of Honshu, has a population of around 7.3 million people; of the five prefectures, Okayama and Hiroshima face the Seto Inland Sea, which separates Honshu and Shikoku, while Tottori and Shimane face the Sea of Japan. Yamaguchi, on the edge of Honshu, faces both seas.
The Chugoku region is a fascinating area where you can enjoy history, culture and spectacular scenery, including Itsukushima Shrine, which is registered as a World Heritage Site, and the Tottori Sand Dunes, one of the largest sand dunes in Japan.
The Seto Inland Sea is the largest body of water separating the main islands. It is dotted with many islands and is known for its beautiful scenery. Petrochemical and steel manufacturing industries have also developed along this coast, and in 1945 Hiroshima became the first city in the world to be hit by an atomic bomb, devastating it, but it has now recovered successfully and become the centre of economic activity in the Chugoku region.
SHIKOKU
Shikoku consists of four prefectures – Kagawa, Tokushima, Ehime and Kochi – and is blessed with a mild climate and 3.8 million inhabitants. 1988 saw the opening of the Great Seto Bridge connecting Mainland and Shikoku, with traffic by car and rail. There are also many ferries operating by sea. The area is full of natural and historical sights, from classic spots such as Shodoshima Island and Dogo Onsen to famous historic castles and shrines, and places where you can experience activities such as whale watching.Winters are relatively mild and rainy. The coast is very beautiful with plenty of coral and tropical fish.
Shikoku’s most famous pilgrimage route, the 88 sacred sites of Shikoku, can be visited from one end of the island to the other. It is a walk around the 88 sacred sites of for the purpose of prayer. The 88 temples are visited in order from the first temple, Reizanji, to the last, Okuboji. When the tour reaches the end, it is called ‘yugan’ or ‘mangan’.
In Tokushima,Awa Odori festival is held throughout every year during the Obon season(Summer). Shikoku is also home to clear emerald-green rivers such as the Shimanto River and Niyodo River.
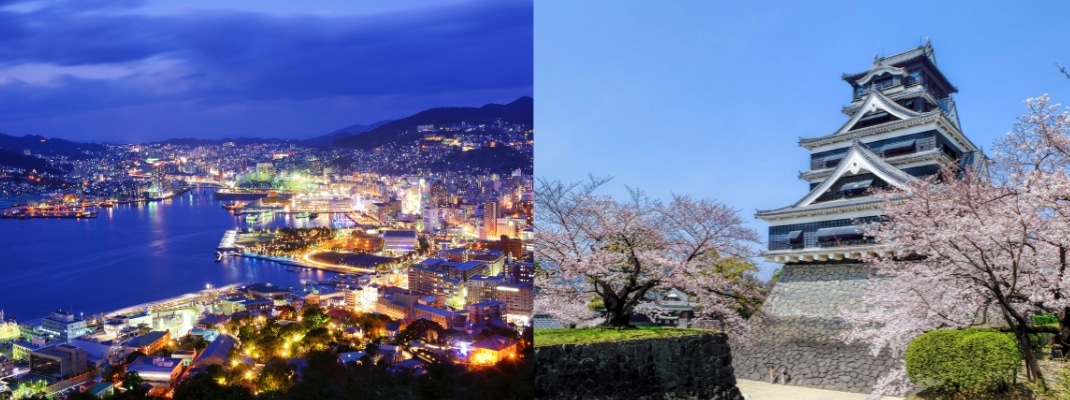
KYUSHU・OKINAWA
The Kyushu-Okinawa region has a population of approximately 14.3 million. It comprises eight prefectures – Fukuoka, Saga, Nagasaki, Oita, Kumamoto, Miyazaki, Kagoshima and Okinawa.
There are many volcanoes in Kyushu, such as Mount Aso in Kumamoto Prefecture and Sakurajima in Kagoshima Prefecture, and hot springs are abundant. Areas near volcanoes are designated national parks.
During the Edo period (1603-1868), when the country was closed to the outside world, Nagasaki was the only city allowed to trade with China and the Netherlands. Today, it is visited by many tourists.
Kyushu has many attractive tourist spots, including Beppu Onsen, the largest hot spring in Japan; Miyazaki, with its rich nature and mild climate and Takachiho, a city of myths and legends surrounded by great nature. The southwestern archipelago has a subtropical climate, and its pristine and mysterious nature can be enjoyed through trekking.
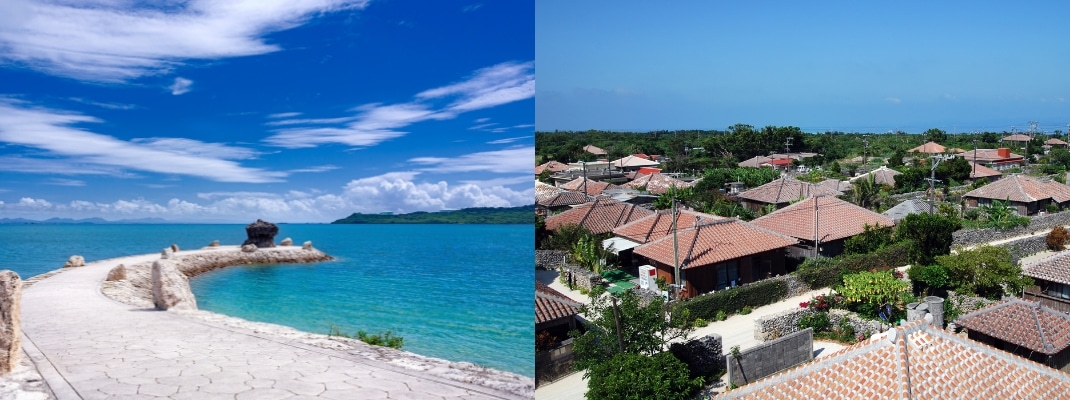
Okinawa is a region with a unique culture and history.
Okinawa once flourished as the Ryukyu Kingdom. The Ryukyu Kingdom prospered through trade with Japan, China and Southeast Asia, and developed its own culture and customs.
In 1879, the Ryukyu Kingdom was abolished by the Japanese Meiji Government and Okinawa Prefecture was established.
After World War II, Okinawa came under US administration, but was returned to Japan in 1972.
Coast of Okinawa is a subtropical archipelago far south of Kyushu, where pineapples and other food crops are grown. It is surrounded by coral reefs and has a very beautiful natural environment.
Get to Know Japan for your Great Adventure
Knowing about the characteristics of each of Japan’s regions can help you create an efficient and purposeful itinerary when on a road trip. Once you are familiar with the regions of Japan, you can explore any areas that interest you in more detail and discover many fascinating places to visit on your road trip!
About the Author
Mayumi
I love nature and travel. I have lived and traveled in some countries and seen many cultures. I would love to share stories of Japan so that visitors can learn more about this wonderful and unique culture and have an unforgettable and enjoyable trip.